Patent Application Process In India

Patent Application Process In India
According to Intellectual Property India, filing a patent in India is a structured, step-by-step process. There are different type of Patent and each Type Of Patent Application Filing Procedure Process can be very different from the other.
Patent filing is immensely beneficial for you and your research because, by filing a patent, you can secure it from exploitation by anyone else. Get the appropriate recognition for your efforts, and then use it for humanity by launching your product in the market through your own company. In new amendments to the Indian Patent Act, MSME and women are expedited, which means faster Patent Application Process and lower fees along with the ease of the process from searching, drafting and filing or you can also collaborate with any existing company in your own domain via technology transfer.
Lexgin IP is always here to help end-to-end in the Patent Application Process In India with a quite affordable pricing structure.
Indian Patent Offices
There are four patent offices in India, which divide the country into four parts, and you can apply for a patent in your own jurisdiction area both online and offline.
1. Delhi
2. Mumbai
3. Chennai
4. Kolkata
Lexgin offers services for filing a patent in India as well as international patents in countries such as Germany, South Africa, and many more.
Types of Patent Application In India
In general, there are three types of patent applications:
1. Provisional Application
2. Ordinary Application
3. PCT phase application
Process Of Patent Application In India
Patent filling is a legal procedure that involves various steps. Lexgin guides you and supports you at each step of Patent Application Filing Procedure Process In India.
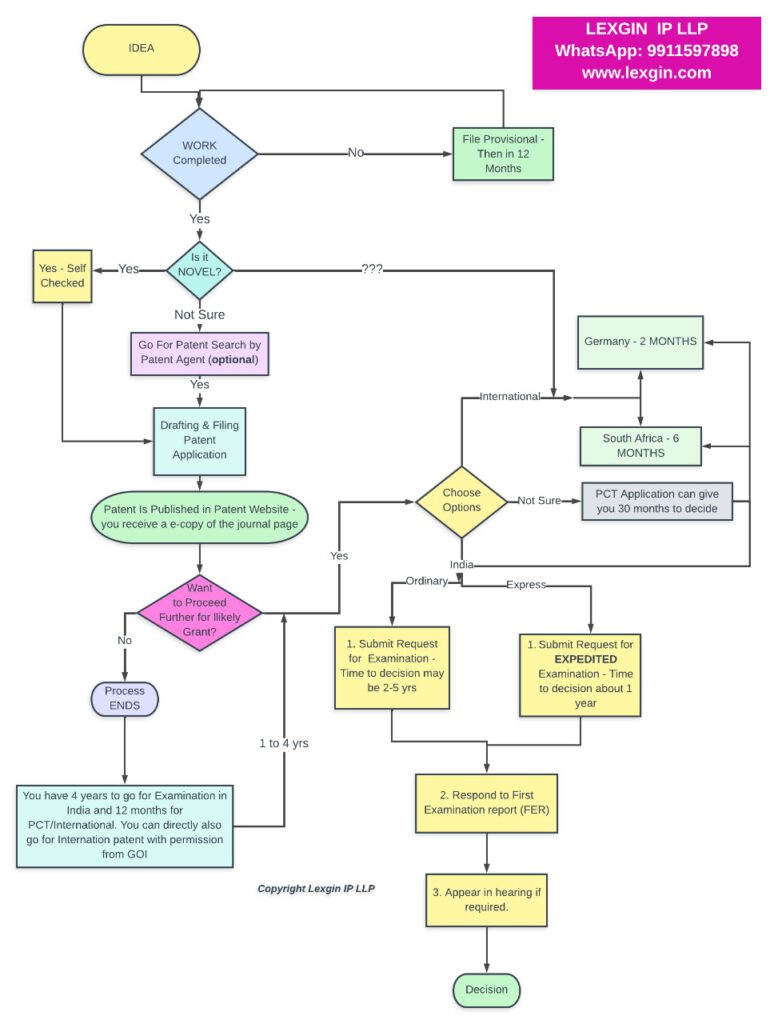
Step 1: Ideation of Innovation
Patent filling is a legal procedure that involves various steps. It is a long road from idea to grant. Collect all the information about your invention; try to fit everything on one sheet of paper. Every necessary document and drawing related to the invention It’s a rough phase; you don’t need to be particular about things; just gather things up and focus on your research. Lexgin IP provides you with specific assistance based on your requirements at this initial stage.
Step 2: Patent Search (Optional)
One of the major issues is How To Search Patent In India? Even though this step is optional, it will greatly reduce your time, expenses, and efforts. You can determine whether your innovation is worth obtaining a patent after doing a novelty and patentability search. This approach makes it crystal evident whether you even need to file a patent at all.
Step 3: Patent Form And Fees and Drafting of Patent Application
A solid patent application involves years of knowledge with patent law and specific training in patent preparation and writing. Just read a few of the domain-related awarded patents to get an idea.
A beginner or unskilled patent writer may overlook numerous guidelines and precautions when crafting claims, comprehensive descriptions, various implementations of the innovation, describing inventive step, etc., and as a result, the patent may not be granted.
It is among the most crucial phases in the cycle of a patent, and a strong patent application prepared by a skilled patent agent or lawyer should be granted a patent after passing all necessary stages of review.
Step 4: Filling of Patent Application:
When one patent is written and reviewed, it is sent to the government’s patent office, where a receipt with the patent filing number is produced.
You can move forward with filing a comprehensive patent application if you have all the necessary information regarding your invention (that is, implementable information) ready with you.
Form 1, 2, 3, 5, 26, 28, as well as other necessary applications must be submitted together with your patent application.
Step 5: Patent Publication
The file is published 18 months after the initial filing once the full specification has been submitted with the patent application. However, you can submit an earlier publication request and pay the required fees if you don’t want to wait until the 18-month period has passed. In most cases, the request for early publication results in the patent application being published one month later.
Step6: Request for examination
The examination of a patent is not automatic, unlike the usual 18-month timeframe that is followed in its publication; instead, the applicant or inventor must seek an inspection.
The inventor must formally ask the patent system to investigate the patent by submitting Form 18 (Forms 18 (A) for accelerated or speedier evaluation for specific applicants). Following the official application, the patent officer conducts a predetermined inspection of your patent application and confirms the following details:
The Patent Act and any applicable laws are used to review the patent application. The requirements for patentability, such as novelty, inventive step, and non-obviousness, as well as industrial applications and patentable subject matter, are looked up and validated.
The examination of a patent is not automatic, unlike the usual 18-month timeframe that is followed in its publication; instead, the applicant or inventor must seek an inspection. The examiner publishes the first examination (FER) with any grounds for objections after the examination of the patent.
The application procedure may be prolonged by another 6–9 months as a result of the examiner’s objections. By submitting Form 4, the inventor may request an extension of time.
Step 7: Respond to FER
Most patent applicants will encounter certain objections, that the initial examination report will indicate (also known as FER). Together with a legal adviser (patent agent), you should examine, comprehend, and write a written answer to the objections made in the assessment report. In an effort to convince the controller that the inventor’s idea is in fact patentable and complies with all patentability requirements, the innovator and patent agent draught and submit a reaction to the examination. If necessary, a live hearing or video conference is scheduled.
Step 8: Grant of a Patent
Assume the examiner finds no objections and is convinced that your invention satisfies all the requirements for patentability. If so, you are given the patent, which is then printed in the “official patent gazette.”
Step 9 – Patent Renewal
Once issued, a patent is subject to periodic renewal requirements. The TRIPS agreement states that India’s maximum patent issuance term is 20 years. Therefore, a 20-year renewal of the patent is required.
Benefits of Filing a Patent:

- With the use of a patent, you have the power to prevent anyone from making, selling, or importing your idea without your consent. Observe intellectual property protection.
- You receive protection for a predetermined time frame, enabling you to fend off competition.
- After that, you can apply your invention yourself.
- As an alternative, you can sell your patent or grant licences for others to utilise it. This might be a significant source of income for your company.
- It’s true that some companies only exist to reap the benefits of a patents they have licenced, sometimes in conjunction with a protected design or trade mark. view the patent licencing process.
















